Dental Health
FILLINGS
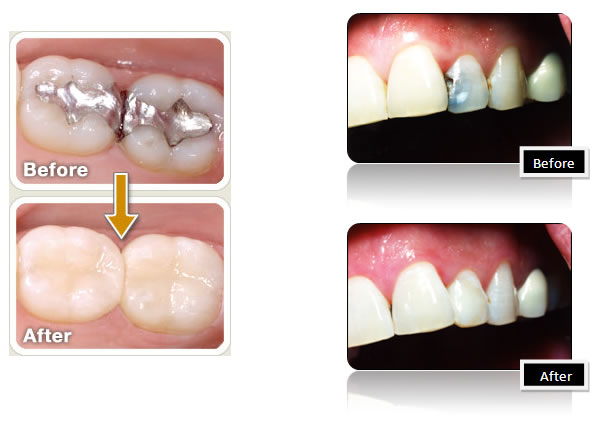
Dental fillings are indicated when there is a structural problem with a tooth. This could have a variety of causes, including tooth decay (cavity) or tooth fracture. A number of materials are available to restore a tooth. Most commonly, teeth are treated with bonded tooth colored composite resin fillings. Caught early enough, cavities can be treated easily and painlessly. If not treated decay can lead to tooth pain and/or infection, necessitating further treatment such as root canal or extraction.
BONDING
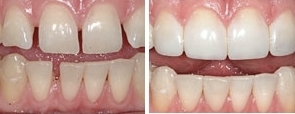
Bonding involves adhering tooth colored composite resin material to the front of the tooth. This procedure is done to repair damage caused by decay, to alter the alignment of the tooth, to close gaps between the teeth, or for other cosmetic purposes. Many shades and translucenies of composite material are available, making it possible to closely match almost any tooth. Bonding allows the dentist to conservatively treat a wide variety of esthetic issues.
SEALANTS
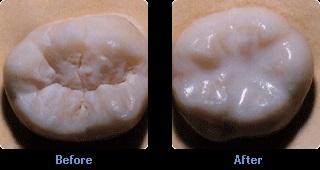
Sealants are a preventative procedure designed to minimize the risk of tooth decay on the chewing surfaces of the teeth (usually the molars). A sealant can be placed by the dentist or the dental hygienest. In this procedure, a resin material is used to fill in narrow grooves and pits on the occulsal (chewing) surface of the tooth. This resin prevents bacteria from entering the grooves or pits, where they could potentially cause decay.
NON-SURGICAL GUM TREATMENTS
The gums, ligaments, and bone around the teeth form the foundation for ones teeth. These structures are referred to as the periodontium. When the periodontium is not healthy, it jeopardizes the teeth just as a bad foundation would threaten the stability of a house. Some signs of unhealthy periodontium (gum disease / periodontial disease) include the following: gums that are red and bleed easily (gingivitis), persistent bad breath, gums that are pulled away from the tooth, loose teeth, and changes in the position or bite of the teeth. Any of these signs may mean something is wrong. With the proper care, however, it may be possible to return them to a healthy state. This is where appropriate gum treatments come in. Initial treatment may involves a deep cleaning or root planing done under a local anesthetic, along with local antibiotic agents. If the gum disease is severe, a referral to a periodontist (gum specialist) may be recommended.
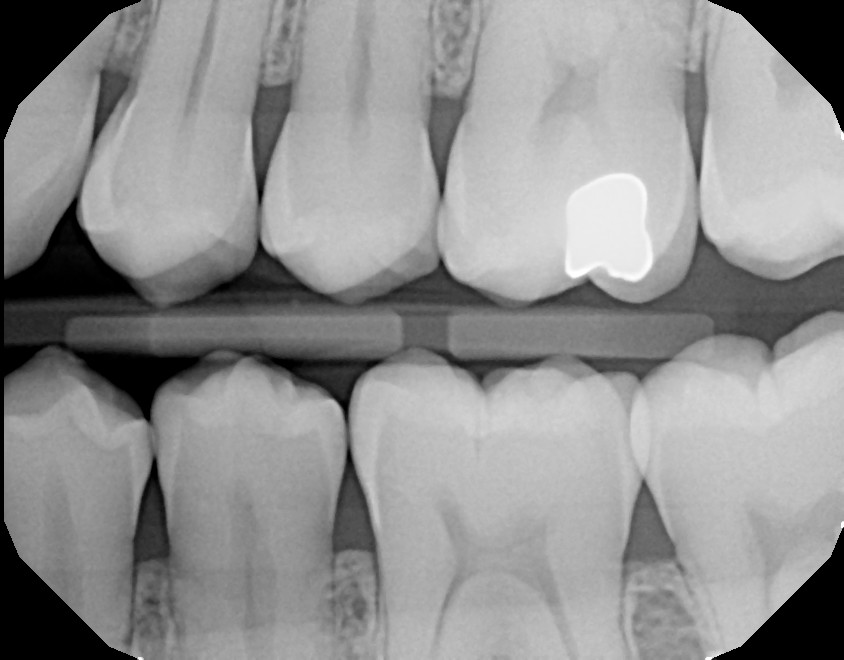
X-RAYS
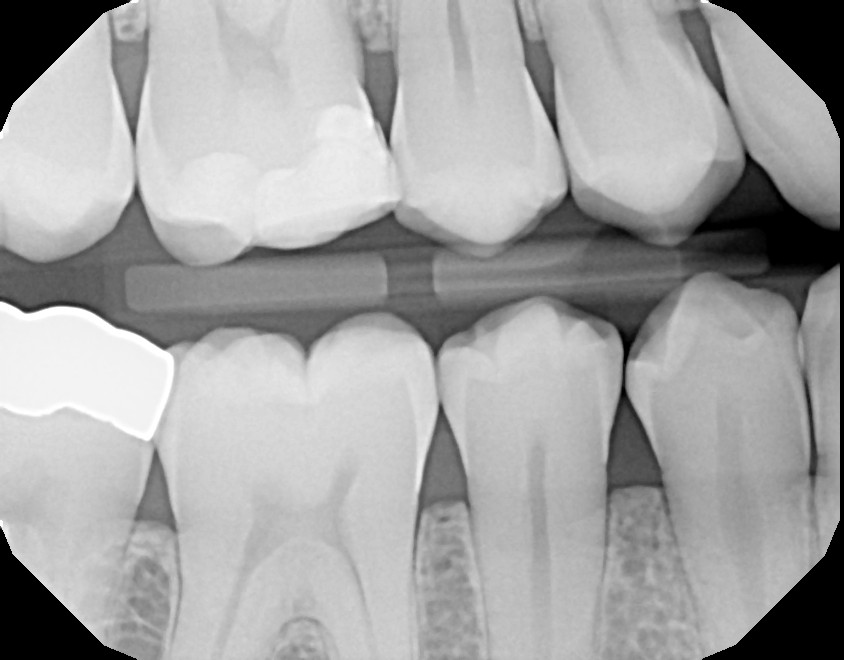
Radiographic images (X-rays), taken digitally, allow the provider to gain valuable information not detectable by visual exam alone. This information is used as part of the diagnostic process to create an accurate and complete treatment plan. Without the benefit of x-ray imaging, hidden problem areas may go undetected. The use of digital sensors (instead of traditional film) drastically reduces patient exposure to radiation. In addition, the speed of imaging is instantaneous, providing greater convenience to the patient and allowing faster diagnosis.
|
